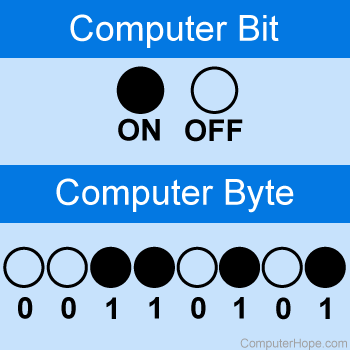
| Bits |
A bit (binary digit) is the smallest unit of data that a computer can process and store |
 |
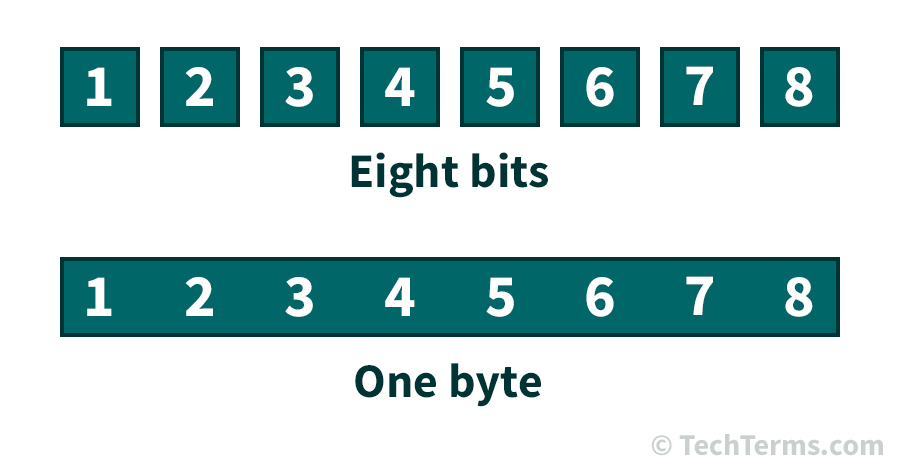
| Bytes |
a group of binary digits or bits (usually eight) operated on as a unit. |
 |
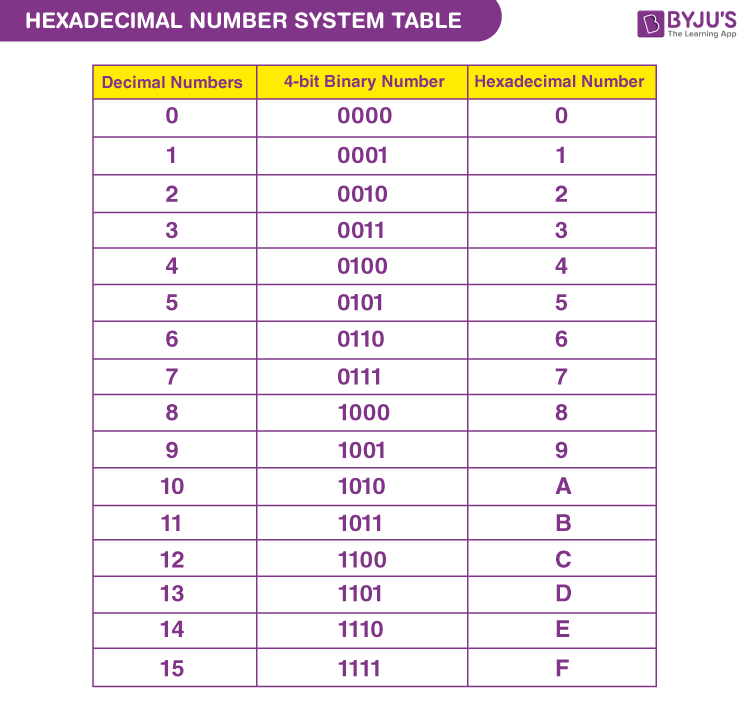
| Hexadecimal |
relating to or using a system of numerical notation that has 16 rather than 10 as its base |
 |
| Nibbles |
a nibble is four consecutive binary digits or half of an 8-bit byte |
|
| Unsigned Integer |
Unsigned Integers (often called “uints”) are just like integers (whole numbers) but have the property that they don’t have a + or - sign associated with them |
 |
| Signed Integer |
A signed integer is a 32-bit datum that encodes an integer in the range [-2147483648 to 2147483647]. |
 |
| Floating Point |
denoting a mode of representing numbers as two sequences of bits, one representing the digits in the number and the other an exponent which determines the position of the radix point. |
 |
| Boolean |
a binary variable, having two possible values called “true” and “false.” |
 |
| ASCII |
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is the most common character encoding format for text data in computers and on the internet. |
 |
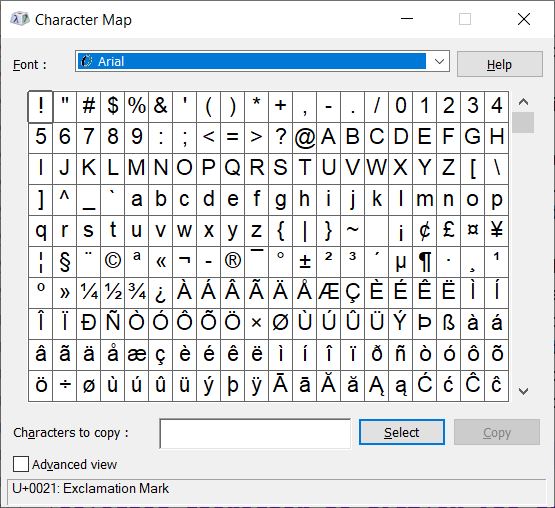
| Unicode |
an international encoding standard for use with different languages and scripts, by which each letter, digit, or symbol is assigned a unique numeric value that applies across different platforms and programs. |
 |
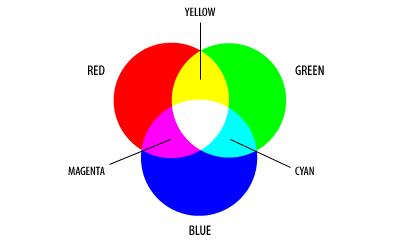
| RGB |
RGB (red, green, and blue) refers to a system for representing the colors to be used on a computer display. |
 |
| Lossy |
A compression scheme in which “useless” or less-than-totally-necessary information is thrown out in order to reduce the size of the data. |
 |
| Lossless |
a data compression algorithm that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data |
 |











